Last updated on May 17th, 2024 at 03:04 am
Who am I? How well you answer the question shows how strong your personal identity and sense of self are. So what is personal identity and sense of self?
I ask myself that question as many times as I can remember and most times, I am confused as to the correct answer.
Not only me, this question has intrigued philosophers, psychologists, and individuals alike throughout history.
Self-perception is a concept deeply intertwined with the human experience and individual personalities.
In this article, we will explore the meaning of personal identity and self-perception, their significance in our lives, and go deeper into practical strategies to achieve a more authentic and fulfilling existence.
Suggested: Understanding Identity Formation
Table of Contents
- What are Personal Identity and Sense of Self?
- Self-concept vs. Self-esteem
- The Components of Sense of Self
- Theories of Personal Identity and Sense of Self
- The Personal Identity Wheel
- Personal Identity Examples
- Factors Influencing Personal Identity and Sense of Self
- Benefits of Personal Identity and Sense of Self
- Strategies for Achieving Sense of Self and Personal Identity
- Tips to Cultivate a Strong Sense of Self
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
What are Personal Identity and Sense of Self?
Individual identity might have variations in its meaning and interpretation, but we are going to go with the generally accepted meaning from psychologists and philosophers.
Personal Identity Definition
It is the unique collection of characteristics, beliefs, values, and experiences that define an individual and distinguish them from others.
For instance, I have several attributes that I know are peculiar to me, and so differentiate me from every other person.
It encompasses your self-perception, including aspects such as personality, interests, cultural background, and life experiences.
It shapes your understanding of who you are, your place in the world, and your relationships with others.
It is a dynamic and evolving construct influenced by internal and external factors, reflecting the ongoing process of self-discovery, self-definition, and the integration of various aspects of your identity into a coherent and stable self-perception.
Related: Balancing Personal Identity and Social Identity
Sense of Self Definition

A sense of self is your subjective perception and understanding of your own identity.
It covers the awareness of your unique characteristics, emotions, thoughts, and experiences, shaping your self-concept and self-esteem.
This internalized self-image influences how you perceive and interact with the world, impacting your behaviours, decisions, and relationships.
A strong self-identity is often associated with confidence, self-awareness, and a clear understanding of personal values and beliefs.
It is a fundamental aspect of human psychology, playing a crucial role in shaping your identity, well-being, and overall psychological development.
Related: What is Identity Foreclosure?
Self-concept vs. Self-esteem
Self-concept
Self-concept is how you perceive yourself as an individual and evaluate yourself, including beliefs, attitudes, and opinions about your own sense of agency, qualities, and characteristics.
It is the overall understanding or awareness you have about yourself, which could be based on your experiences, social interactions, and personal beliefs.
Self-esteem
On the other hand, self-esteem refers to the evaluation or the overall value and worth you place on yourself.
It is the personal judgment or belief about your own value, importance, and competence.
Self-esteem can be influenced by various factors, such as achievements, social comparison, and feedback from others.
While self-concept and self-esteem are related, they have distinct differences.
Self-concept is more focused on the perception and understanding of yourself, including identity, personality traits, and beliefs.
It involves the knowledge and understanding of who you are as an individual.
Self-esteem, on the other hand, is more focused on the judgment and evaluation of yourself, how you feel about yourself, and your overall sense of self-worth.
It is often influenced by external factors, such as societal standards, peer comparison, and feedback from others.
Related: What is Identity Diffusion and What Determines it?
The Components of Sense of Self

The self-identity refers is a multidimensional construct that includes cognitive, emotional, and relational components.
Let’s take a look…
1. Cognitive Aspect of Sense of Self
The cognitive aspect of the self-identity involves self-awareness, self-concept, and self-identity.
- Self-awareness is recognizing one’s thoughts and behaviors.
- Self-concept is the beliefs and ideas about oneself, including personality traits and abilities.
- Self-identity is how a person defines themselves in relation to others and social groups.
2. Emotional Aspect of Sense of Self
The emotional aspect of the self-identity includes self-esteem, self-efficacy, and self-worth.
- Self-esteem reflects feelings of self-worth and acceptance, influenced by achievements and relationships.
- Self-efficacy is the belief in one’s ability to achieve goals, impacting motivation and confidence.
- Self-worth reflects a sense of inherent value and deservingness.
3. Rational Aspect of Sense of Self
The relational aspect of the self-identity involves how individuals relate to others in social contexts. It includes self-identity in relationships, social comparison, and social integration.
- Self-identity in relationships refers to how individuals define themselves in relation to others.
- Social comparison involves evaluating oneself in comparison to others.
- Social integration pertains to the sense of belongingness and acceptance within social groups.
Also Read: Personal Agency: The Pillar of Every Personality
Theories of Personal Identity and Sense of Self

There are several theories of self-identity that attempt to answer the fundamental question of what makes a person the same individual over time.
Here are a few of the most prominent theories:
Psychological Continuity Theory: This theory suggests that self-identity is determined by the continuity of a person’s psychological states, experiences, memories, and beliefs. According to this view, if a person’s memories and psychological traits remain consistent over time, they are considered to be the same individual.
Physical Continuity Theory: This theory asserts that a sense of self is tied to the continuity of the physical body. It suggests that if the physical body remains the same or gradually changes over time, the person remains the same individual.
Related: How to Snap out of Identity Moratorium Quickly
Biological Theory: This theory identifies individual identity with biological factors, such as genes or the physical and chemical elements that constitute a living organism. It argues that an individual’s biological continuity determines their identity.
Bundle Theory: Rather than identifying self-perception with a single entity, bundle theory argues that a person’s identity is a collection or bundle of various characteristics, traits, experiences, and memories. According to this view, one’s identity is a combination of multiple factors rather than a single defining aspect.
Narrative Theory: This theory emphasizes the importance of storytelling and narrative in identifying an individual. It suggests that individual identity is constructed through the continuous narrative that individuals create about their lives, incorporating their experiences, memories, and relationships.
4D Theory: This theory introduces the concept of four-dimensionalism, considering self-perception as a continuous temporal entity. It suggests that your identity comprises various temporal stages linked by causal connections.
Related: Tips and Tools to Build Professional Identity
The Personal Identity Wheel
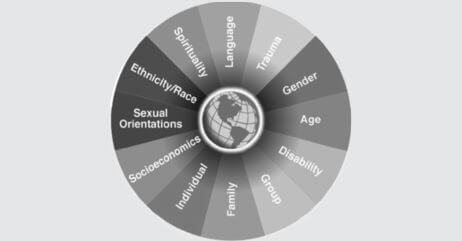
The Personal Identity Wheel is a tool used to explore and understand various aspects of a person’s identity.
It is a circular diagram divided into segments that represent different dimensions of identity, such as race, gender, abilities, religion, and interests.
Each segment is further divided into inner and outer rings. The inner ring signifies how a person perceives themselves in that aspect of their identity, while the outer ring represents how society perceives them.
By reflecting on the different dimensions of their identity, individuals can gain insight into how these aspects of themselves shape their experiences and interactions with others.
Related: The Role of Personality in Career Choices
Personal Identity Examples
Gender: Your gender identity, whether male, female, or non-binary, is a fundamental aspect of your identity. It encompasses how you perceive and express your own gender.
Nationality: Your nationality or citizenship indicates the country or countries to which you belong. It is often determined by place of birth, ancestry, or legal documentation.
Ethnicity: Your ethnicity reflects your cultural and ancestral background. It includes elements such as race, language, traditions, and customs.
Religion: Your religious beliefs and practices shape your identity. It can encompass various faiths, ideologies, or atheism.
Physical Appearance: Your physical characteristics, including features like hair color, eye color, height, and body shape, contribute to your identity.
Family and Relationships: Your familial connections, such as being a parent, sibling, or spouse, form an important part of your individual identity. Your relationships with friends, colleagues, and community members also shape your identity.
Education and Occupation: The level of education you have attained and your chosen occupation contribute to your identity. It reflects your skills, knowledge, and professional achievements.
Personal Interests and Hobbies: Your personal interests, such as hobbies, sports, arts, and cultural activities, help define your identity. This includes the things that you are passionate about and enjoy doing in your leisure time.
Personality Traits: Your unique qualities, strengths, weaknesses, and temperament are part of your self-perception. This includes characteristics like introversion or extroversion, empathy, creativity, and more.
Personal Values and Beliefs: Your values, ethics, and key beliefs shape your identity. They guide your behaviour, decision-making, and how you relate to the world around you.
Related: What is Identity Achievement?
Factors Influencing Personal Identity and Sense of Self

1. Social Factors
Cultural and Societal Impact: The culture and society in which you grow up significantly influence your identity. Cultural beliefs, values, and traditions shape how you perceive yourself and others. For example, collectivist cultures emphasize group identity, while individualistic cultures prioritize personal achievements and autonomy.
Influence of Family and Peer Groups: Family and peer groups play a crucial role in shaping self-perception. Family upbringing, values, and experiences shape your beliefs and attitudes, influencing what you finally become. Similarly, peer groups influence your identity through shared interests and social norms, providing a sense of belonging and shared identity.
2. Psychological Factors
Personality Traits: Personality traits like introversion or extroversion can impact personal identity and sense of self. Introverted individuals may see themselves as reflective, while extroverts may view themselves as outgoing and sociable, influencing how they interact with others.
Childhood Experiences and Development: Childhood experiences and upbringing significantly shape individual identity, including self-worth and self-esteem. Supportive environments can encourage self-confidence and self-worth.
Social Comparison and Self-perception: Social comparison significantly impacts individuality and self-concept. Individuals seek validation and belonging by comparing achievements and appearance to others, shaping self-perception and identity.
3. Environmental Factors
Geographical and Locational Influence: Geographical location influences how you identify yourself, shaping your lifestyle, interests, and values. Rural living may encourage a connection to nature, while urban living may emphasize a fast-paced lifestyle.
Educational and Professional Backgrounds: Education and professional experiences significantly impact self persona, shaping values, and aspirations, and providing a sense of competence and accomplishment.
Benefits of Personal Identity and Sense of Self
- Genuine relationships and emotional connections fostered by authenticity and self-awareness enhance well-being and fulfillment.
- Self-acceptance and a positive self-image contribute to emotional well-being and mental health.
- Your individual identity promotes resilience by enabling individuals to face challenges and adapt to change effectively.
- Emotional regulation and coping strategies are bolstered by a strong self-perception and individual identity.
- Self-persona fuels motivation and goal achievement, leading to a sense of empowerment and accomplishment.
- Self-efficacy and empowering beliefs are nurtured by a strong sense of self-persona and self-worth.
Strategies for Achieving Sense of Self and Personal Identity
Identity achievement is a lifelong process that requires self-reflection, exploration, and personal growth.
Here are some strategies that can help individuals in their journey towards identity achievement:
1. Self-reflection: Engage in regular self-reflection by exploring your values, beliefs, and goals. This can involve keeping a journal, talking with trusted friends or family members, or seeking out professional support.
2. Exploration: Try new experiences and activities that can help you discover your interests, strengths, and weaknesses. This can involve taking on new hobbies, volunteering, or traveling to new places.
3. Education: Seek out education and training opportunities that align with your interests and goals. This can involve taking courses, attending workshops, or pursuing a degree.
4. Support System: Surround yourself with supportive individuals who encourage and challenge you to grow. This can involve joining a community group, a mentorship program, or seeking out therapy or counseling.
5. Embrace Challenges: Embrace challenges and life circumstances as opportunities for growth and learning. Use these experiences to gain new insights and perspectives on yourself and your values.
6. Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness and self-awareness by staying present in the moment and observing your thoughts and emotions without judgment. This can involve meditation, yoga, or other mindfulness practices.
7. Set Goals: Set achievable goals for yourself that align with your values and interests. This can involve creating a vision board, setting SMART goals, or creating an action plan.
8. Boundaries and Assertiveness: Boundaries and assertiveness are crucial strategies for developing personal identity, as they help individuals define their values, needs, and limits while expressing themselves confidently and respectfully.
Tips to Cultivate a Strong Sense of Self
- Self-reflection: Take time to understand your values, beliefs, and aspirations.
- Set boundaries: Define your limits and communicate them assertively.
- Embrace individuality: Celebrate your unique qualities and experiences.
- Seek support: Surround yourself with positive and supportive relationships.
- Pursue passions: Engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
- Practice self-care: Prioritize your physical, emotional, and mental well-being.
- Continuous learning: Embrace growth and self-improvement through new experiences and knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is personal identity?
It covers your unique characteristics, beliefs, values, and experiences that define who you are and distinguish them from others.
What is an example of a sense of self?
An example is an individual recognizing their own personality traits, values, and beliefs, shaping their self-concept and self-esteem.
What is the sense of self?
It refers to your subjective perception and understanding of your own identity, including your unique characteristics, emotions, thoughts, and experiences.
What is a term for your sense of self?
A term for it is self-concept, encapsulating an individual’s beliefs and perceptions about themselves.
What is the sense of self in human development?
In human development, it is the evolving understanding of one’s identity, encompassing self-awareness, self-esteem, and self-perception.
What makes up your personal identity?
It is comprised of an individual’s cultural background, experiences, beliefs, values, and social roles, shaping their unique self-perception.
What is personal identity best described as?
It is best described as the collection of characteristics, beliefs, values, and experiences that define an individual’s unique self-perception.
Final Thoughts
Personal identity and self-perception are personal constructs that define your understanding of yourself.
Shaped by cultural influences, experiences, and relationships, they form the core of your being.
Embracing and understanding these aspects is crucial for personal growth, resilience, and well-being.
By recognizing the significance of personal identity and nurturing a positive sense of self, you can navigate life’s complexities with authenticity, confidence, and a strong foundation of self-awareness.
References:
- https://psychcentral.com/relationships/why-you-need-a-strong-sense-of-self-and-how-to-boost-it
- https://growtherapy.com/blog/what-is-self-concept-in-psychology/
- https://www.mindbodygreen.com/articles/how-to-develop-your-sense-of-self
- https://www.betterhelp.com/advice/general/the-importance-of-a-strong-sense-of-self-and-how-to-gain-it/
Pyo Merez (PsyD) is a distinguished adolescent and adult psychologist at the forefront of mental health advocacy.
With expertise in cognitive and developmental psychology, focusing on social relationships, cultural contexts, and individual differences, Pyo has dedicated his career to empowering adolescents and adults.
As a sought-after speaker and panelist, Pyo shares invaluable insights on issues affecting young people, contributing to a deeper understanding of mental health and well-being in today's society.


